Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Cloud computing is all about accessing and using computer resources and services over the internet, just like electricity from a power grid.
- These resources can include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more.
- Instead of hosting these resources on your local device or data center, you rent them from a cloud service provider.
Understanding Cloud Service Models and Deployment Models
- In the world of cloud computing, two key concepts shape the landscape: cloud service models and deployment models.
- These concepts serve as the foundation for how businesses and individuals access and utilize cloud resources.
- In this blog, we’ll delve into these important aspects of cloud computing to provide a clear understanding of how they work.
Cloud Service Models:
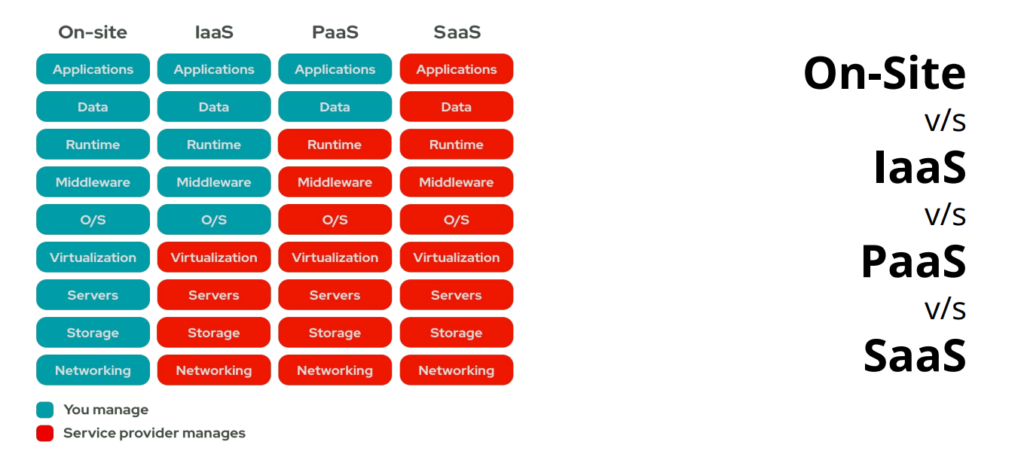
Cloud service models, also known as cloud computing service models, define the type of services offered by cloud providers.
There are three primary service models:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): AWS, Rackspace, MS Azure etc.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku etc.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Google drive, Google docs, MS Office 365 etc
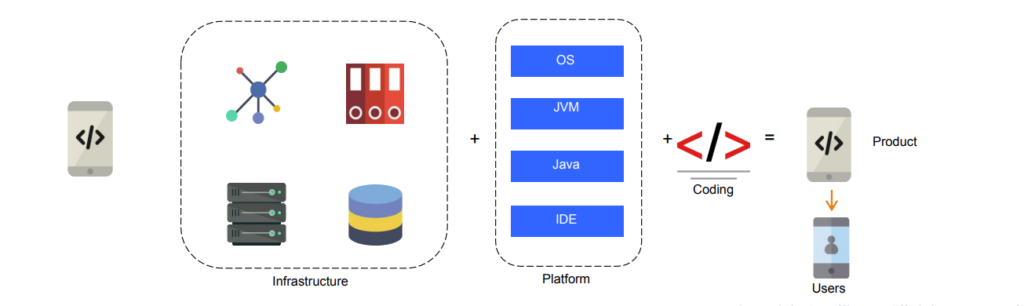
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- IaaS is the most fundamental cloud service model.
- It provides users with virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking resources, allowing them to create and manage their own virtualized infrastructure.
- This model offers maximum flexibility, as users are responsible for managing their operating systems, applications, and data.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- PaaS takes a step further by offering a complete development and deployment environment in addition to infrastructure resources.
- With PaaS, users can build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- This streamlines application development and allows developers to focus on coding and innovation rather than infrastructure management.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS):
- SaaS is the most user-friendly cloud service model.
- It delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
- Users can access the software through a web browser without the need for installation or maintenance.
- Common examples of SaaS include email services like Gmail, collaboration tools like Microsoft 365, and customer relationship management (CRM) software like Salesforce.
Cloud Deployment Models:
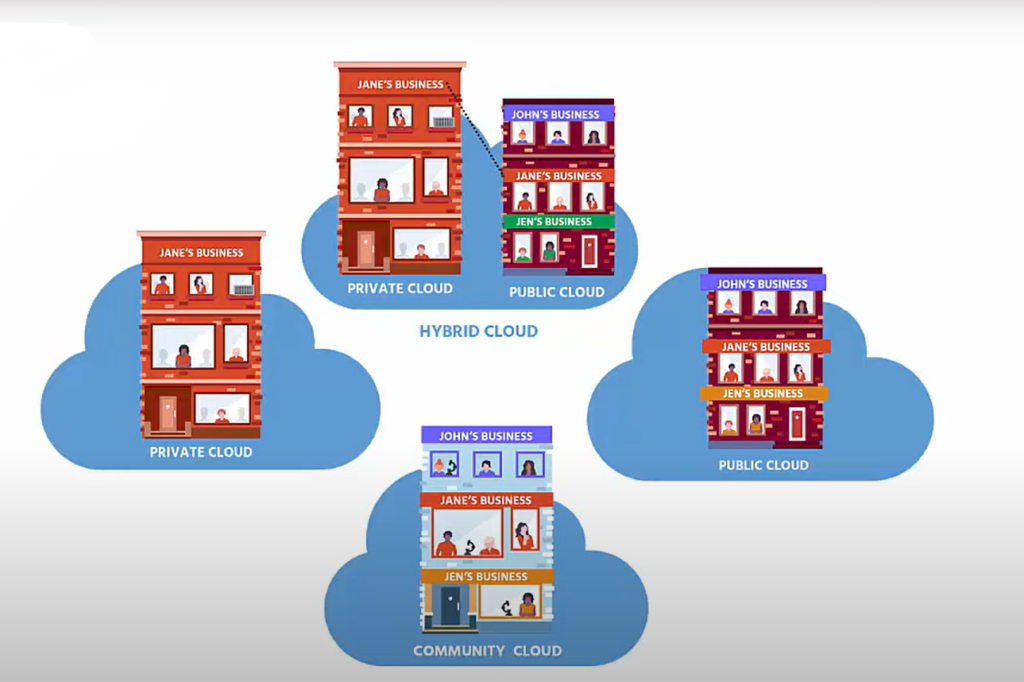
Cloud deployment models, on the other hand, define where and how cloud services are hosted and made available.
There are four primary deployment models:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Community Cloud
1. Public Cloud:

- The public cloud is the most common and easily accessible deployment model.
- In this model, cloud resources are owned and managed by third-party cloud service providers and made available to the general public or organizations.
- These providers deliver services like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS to users over the Internet.
- Public clouds are highly scalable and cost-effective, making them an attractive option for a wide range of users.
2. Private Cloud:

- Private clouds are typically used by a single organization or entity.
- They can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party cloud provider.
- Private clouds offer greater control, security, and customization, making them suitable for businesses with specific regulatory or security requirements.
3. Hybrid Cloud:
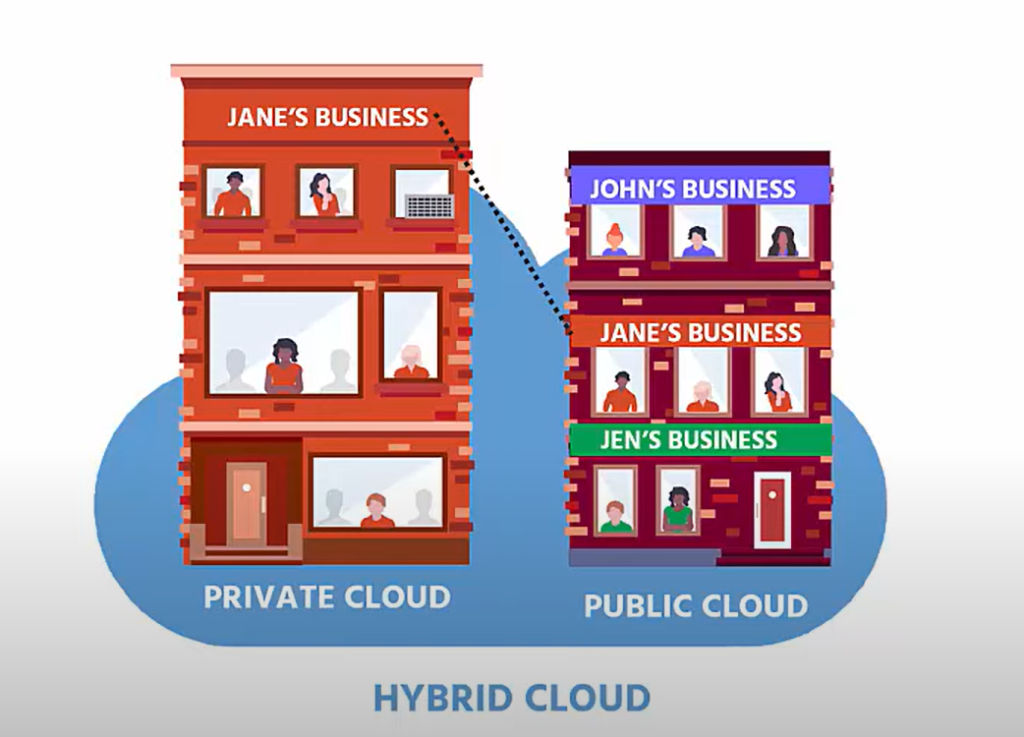
- Hybrid clouds merge the characteristics of both public and private clouds, facilitating the sharing of data and applications seamlessly across these two distinct environments.
- This model offers flexibility and allows organizations to take advantage of the cost-efficiency of public cloud resources while keeping sensitive data on a private cloud for security and compliance reasons.
4. Community Cloud:
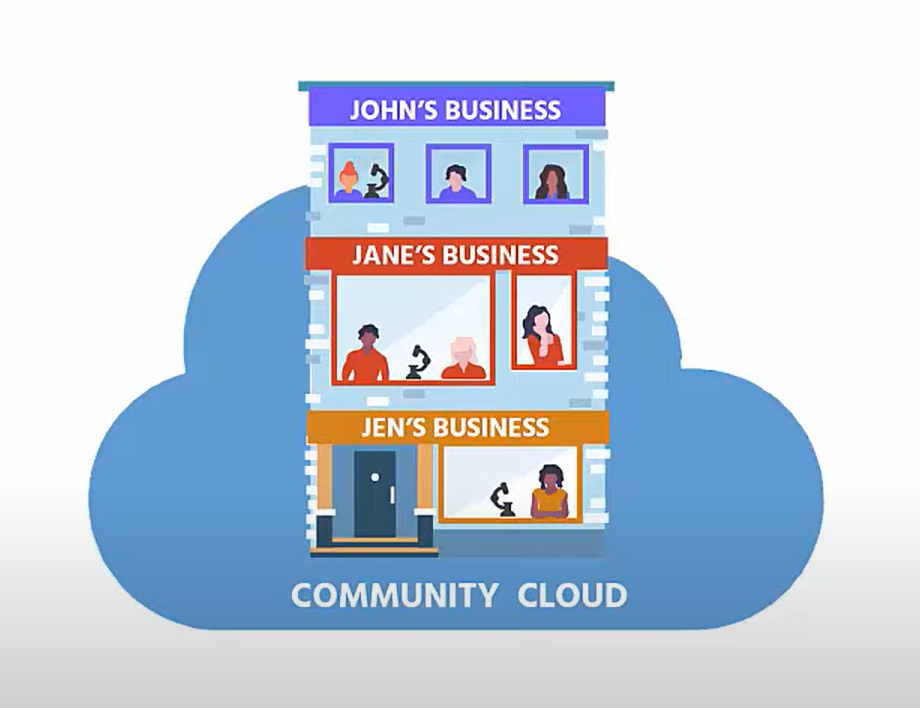
- Community clouds are shared by multiple organizations with common concerns, such as compliance or industry-specific needs.
- These organizations collaborate to build and maintain the community cloud, providing a cost-effective way to meet their unique requirements.
Conclusion:
- In conclusion, understanding cloud service models and deployment models is crucial for making informed decisions when adopting cloud computing.
- Organizations can choose the right service model based on their specific requirements, whether they need full control over infrastructure or seek a hassle-free software solution.
- Similarly, selecting the appropriate deployment model depends on factors like security, compliance, and scalability needs.
- By grasping these concepts, businesses and individuals can harness the full power of cloud computing to streamline their operations and drive innovation.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: Cloud resources can be easily scaled up or down to meet your specific needs.
- Cost-Efficiency: Pay only for the resources you use, eliminating the need for large upfront infrastructure investments.
- Flexibility: Enjoy the freedom to access your data and applications from any location with an internet connection.
- Reliability: Cloud service providers offer high levels of uptime and redundancy.
Examples of Cloud Computing:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- Example: Netflix
- Netflix relies on AWS to deliver its streaming services to millions of users worldwide. AWS provides the necessary infrastructure to ensure smooth playback and uninterrupted service.
2. Microsoft Azure:
- Example: Toyota Racing Development (TRD)
- TRD uses Azure to process and analyze massive amounts of data from race cars in real-time, enabling them to make informed decisions during races.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Example: Spotify
- Spotify uses GCP to host and deliver its music streaming service, leveraging GCP’s global network to ensure low latency and high availability.
4. Software as a Service (SaaS):
- Example: Microsoft 365
- Microsoft 365 provides a suite of productivity tools like Word, Excel, and Outlook through the cloud. Users can access these applications from any device with internet access.
5. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- Example: Heroku
- Developers use Heroku’s PaaS platform to deploy and manage web applications easily, without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
6. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- Example: DigitalOcean
- DigitalOcean offers virtual machines and storage in the cloud, allowing developers to create and manage their infrastructure.
7. Cloud Storage:
- Example: Google Drive, Dropbox
- These cloud storage solutions allow you to store your files, photos, and documents securely on remote servers, accessible from any device with internet access.
8. Web-Based Email:
- Example: Gmail, Outlook
- These email services store your messages and attachments in the cloud, enabling you to access your email from any device with a web browser.
Real-World Scenarios
Here are some real-world scenarios that demonstrate the practical applications of cloud computing:
1. E-commerce Scalability:
Scenario: Imagine you own an e-commerce website, and you’ve just launched a flash sale. The sudden influx of visitors and transactions requires more server resources than usual. In a traditional setup, this could lead to website crashes and lost sales. However, with cloud computing, you can automatically scale up your server capacity to handle the increased demand in real time. For example, Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides services like Amazon EC2 and Auto Scaling, which allow your website to handle traffic spikes seamlessly.
2. Data Analytics for Healthcare:
Scenario: A medical research institution needs to analyze vast datasets to identify patterns in patient records and make breakthroughs in disease research. Setting up and maintaining an on-premises high-performance computing cluster for this purpose would be expensive and time-consuming. Instead, they can utilize cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud to access powerful data analytics tools and scalable compute resources, making it easier to process large volumes of healthcare data efficiently.
3. Disaster Recovery for Small Businesses:
Scenario: A small business relies on its IT infrastructure to manage operations. In case of a server failure or data loss due to unforeseen circumstances, the business could face severe disruptions. By implementing cloud-based disaster recovery solutions, such as those offered by AWS or Azure, the business can automatically back up its data and applications to the cloud. In the event of a disaster, they can swiftly recover their operations from the cloud, minimizing downtime and data loss.
4. Remote Work Collaboration:
Scenario: Many organizations have adopted a remote work model, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. Cloud-based collaboration tools like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace have become indispensable. Employees can access documents, emails, and collaborative software from anywhere, ensuring seamless teamwork and productivity regardless of location. Cloud computing makes it possible for teams to work together in real-time, sharing files and information securely.
5. Streaming Entertainment Services:
Scenario: Companies like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ provide high-quality streaming video content to millions of subscribers. To ensure a smooth and buffer-free experience for users, they leverage cloud infrastructure. Cloud providers like AWS offer Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to deliver content from servers located closer to the end-users, reducing latency and improving streaming quality. This scalability and reliability are vital to the success of such services.
6. Internet of Things (IoT) Data Processing:
Scenario: IoT devices, like smart thermostats or fitness trackers, generate enormous volumes of data. Processing and analyzing this data in real-time is a complex task. Cloud platforms, such as AWS IoT or Azure IoT, offer solutions to collect, store, and process IoT data. For example, a smart city can use cloud computing to analyze data from sensors to improve traffic management, energy efficiency, and public safety.
7. Content Delivery for Gaming:
Scenario: Online gaming companies require low-latency and high-performance infrastructure to deliver real-time gaming experiences to players. Cloud providers, like Google Cloud and Amazon GameLift, offer services that enable game developers to host and scale their games in the cloud, ensuring smooth gameplay experiences and quick matchmaking for players.
These scenarios showcase the versatility and impact of cloud computing across various industries and use cases. Cloud technology is not only scalable but also highly adaptable, making it an essential tool for businesses and organizations aiming to meet the demands of a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing is a game-changer in technology, providing accessible, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of applications. As demonstrated by the examples above, organizations across different industries are harnessing the power of the cloud to improve efficiency and scalability. Embracing cloud computing can empower your business or project to reach new heights in today’s digital age.